深入informer
Informer介绍
client-go中提供的informer主要用来监听k8s资源的创建、删除、更新操作,通过事件回调交给controller进一步处理。
informer整体机制如下图:
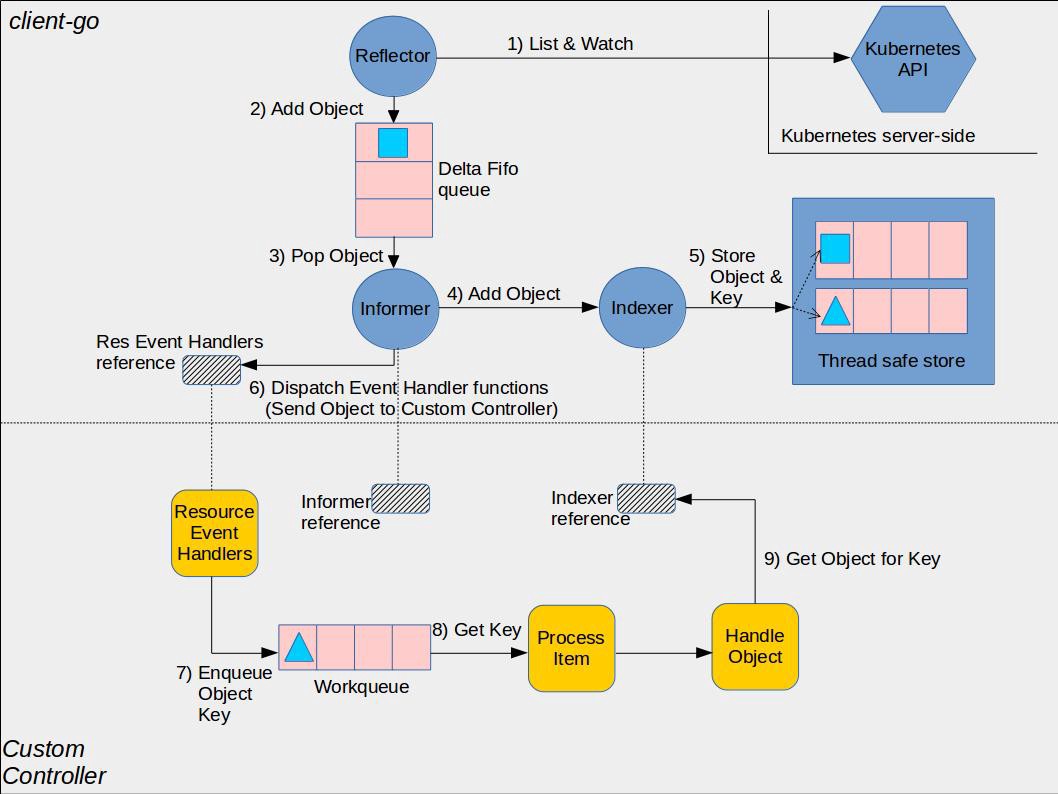
(from client-go under the hood)
上半部分是由client-go实现的,而下半部分黄色图标需要开发者自行实现逻辑,在使用kubebuilder进行controller开发时,框架会自动实现这部分,开发者只需专注Reconcile逻辑。
Reflector:用于Watch指定的kubernetes资源,当资源发生变化时,比如Added、Modified、Deleted调用DeltaFIFO将资源对象与DeltaType存储起来。
DeltaFIFO: 先进先出队列,用于存储资源变化类型及对应资源对象,DeltaType有Added、Updated、Deleted、Sync等;其Pop方法会将队列中的资源对象取出并调用informer注册的函数进行处理。
Indexer:kubernetes资源对象缓存,可以直接从本地缓存读取对象,减少对apiserver的访问;在DeltaFIFO Pop的处理中,将对象资源进行存储、更新、删除。
深入Informer
让我们从NewSharedIndexInformer一起看一下informer的具体实现,Shared Infomer对同一种资源共用一个Reflector,从而减少apiserver负载。
1 新建Informer
NewSharedIndexInformer初始化sharedIndexInformer,主要包括注册、处理分发回调事件的processor、新建Indexer、listerWatcher接口实现。
func NewSharedIndexInformer(lw ListerWatcher, exampleObject runtime.Object, defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod time.Duration, indexers Indexers) SharedIndexInformer {
realClock := &clock.RealClock{}
sharedIndexInformer := &sharedIndexInformer{
// 注册、处理回调函数
processor: &sharedProcessor{clock: realClock},
// 创建indexer
indexer: NewIndexer(DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc, indexers),
// 实现具体的listwatch接口
listerWatcher: lw,
// 资源对象
objectType: exampleObject,
resyncCheckPeriod: defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod,
defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod: defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod,
cacheMutationDetector: NewCacheMutationDetector(fmt.Sprintf("%T", exampleObject)),
clock: realClock,
}
return sharedIndexInformer
}
看一下Indexer的具体实现,简单来说是使用 map + sync.RWMutex 实现了Indexer接口。
// NewIndexer returns an Indexer implemented simply with a map and a lock.
func NewIndexer(keyFunc KeyFunc, indexers Indexers) Indexer {
return &cache{
cacheStorage: NewThreadSafeStore(indexers, Indices{}),
// 哈希函数
keyFunc: keyFunc,
}
}
// NewThreadSafeStore creates a new instance of ThreadSafeStore.
func NewThreadSafeStore(indexers Indexers, indices Indices) ThreadSafeStore {
return &threadSafeMap{
items: map[string]interface{}{},
indexers: indexers,
indices: indices,
}
}
// threadSafeMap implements ThreadSafeStore
type threadSafeMap struct {
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices
}
2 sharedIndexInformer.Run,完成DeltaFIFO、controller新建,运行processor.run、controller.Run
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
// 新建DeltaFIFO,作为Queue传入Controller
fifo := NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(DeltaFIFOOptions{
KnownObjects: s.indexer,
EmitDeltaTypeReplaced: true,
})
cfg := &Config{
// 作为参数传入Reflector
Queue: fifo,
ListerWatcher: s.listerWatcher,
ObjectType: s.objectType,
FullResyncPeriod: s.resyncCheckPeriod,
RetryOnError: false,
ShouldResync: s.processor.shouldResync,
// DeltaFIFO Pop时的处理函数
Process: s.HandleDeltas,
WatchErrorHandler: s.watchErrorHandler,
}
// 新建controller
func() {
s.startedLock.Lock()
defer s.startedLock.Unlock()
s.controller = New(cfg)
s.controller.(*controller).clock = s.clock
s.started = true
}()
// Separate stop channel because Processor should be stopped strictly after controller
processorStopCh := make(chan struct{})
var wg wait.Group
defer wg.Wait() // Wait for Processor to stop
defer close(processorStopCh) // Tell Processor to stop
wg.StartWithChannel(processorStopCh, s.cacheMutationDetector.Run)
// 运行processor分发回调
wg.StartWithChannel(processorStopCh, s.processor.run)
defer func() {
s.startedLock.Lock()
defer s.startedLock.Unlock()
s.stopped = true // Don't want any new listeners
}()
// 执行controller
s.controller.Run(stopCh)
}
// NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions returns a Queue which can be used to process changes to
// items. See also the comment on DeltaFIFO.
func NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(opts DeltaFIFOOptions) *DeltaFIFO {
if opts.KeyFunction == nil {
opts.KeyFunction = MetaNamespaceKeyFunc
}
f := &DeltaFIFO{
// 存储资源对象
items: map[string]Deltas{},
// fifo队列,pop从这里取key,再到map中取值
queue: []string{},
keyFunc: opts.KeyFunction,
knownObjects: opts.KnownObjects,
emitDeltaTypeReplaced: opts.EmitDeltaTypeReplaced,
}
f.cond.L = &f.lock
return f
}
type Delta struct {
// 变化类型
Type DeltaType
// 资源对象
Object interface{}
}
3 controller.Run 新建Reflector、运行Reflector.Run,执行informer主要逻辑processLoop
// Run begins processing items, and will continue until a value is sent down stopCh or it is closed.
// It's an error to call Run more than once.
// Run blocks; call via go.
func (c *controller) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
go func() {
<-stopCh
c.config.Queue.Close()
}()
// c.config.Queue即为DeltaFIFO
r := NewReflector(
c.config.ListerWatcher,
c.config.ObjectType,
c.config.Queue,
c.config.FullResyncPeriod,
)
r.ShouldResync = c.config.ShouldResync
r.WatchListPageSize = c.config.WatchListPageSize
r.clock = c.clock
if c.config.WatchErrorHandler != nil {
r.watchErrorHandler = c.config.WatchErrorHandler
}
c.reflectorMutex.Lock()
c.reflector = r
c.reflectorMutex.Unlock()
var wg wait.Group
wg.StartWithChannel(stopCh, r.Run)
wait.Until(c.processLoop, time.Second, stopCh)
wg.Wait()
}
4 Reflector.Run 实现对资源的list、watch,并在watch到资源变化后,调用watchHandler,对不通的事件类型调用DeltaFIFO
func (r *Reflector) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
klog.V(2).Infof("Starting reflector %s (%s) from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.resyncPeriod, r.name)
wait.BackoffUntil(func() {
// 执行list、watch,并调用watchHandler
if err := r.ListAndWatch(stopCh); err != nil {
r.watchErrorHandler(r, err)
}
}, r.backoffManager, true, stopCh)
klog.V(2).Infof("Stopping reflector %s (%s) from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.resyncPeriod, r.name)
}
// ListAndWatch 除List(分页机制)、Watch还有调用DeltaFIFO的Resync机制
func (r *Reflector) ListAndWatch(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
klog.V(3).Infof("Listing and watching %v from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.name)
var resourceVersion string
// List资源
options := metav1.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: r.relistResourceVersion()}
if err := func() error {
initTrace := trace.New("Reflector ListAndWatch", trace.Field{"name", r.name})
defer initTrace.LogIfLong(10 * time.Second)
var list runtime.Object
var paginatedResult bool
var err error
listCh := make(chan struct{}, 1)
panicCh := make(chan interface{}, 1)
go func() {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
panicCh <- r
}
}()
// Attempt to gather list in chunks, if supported by listerWatcher, if not, the first
// list request will return the full response.
pager := pager.New(pager.SimplePageFunc(func(opts metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return r.listerWatcher.List(opts)
}))
switch {
case r.WatchListPageSize != 0:
pager.PageSize = r.WatchListPageSize
case r.paginatedResult:
// We got a paginated result initially. Assume this resource and server honor
// paging requests (i.e. watch cache is probably disabled) and leave the default
// pager size set.
case options.ResourceVersion != "" && options.ResourceVersion != "0":
// User didn't explicitly request pagination.
//
// With ResourceVersion != "", we have a possibility to list from watch cache,
// but we do that (for ResourceVersion != "0") only if Limit is unset.
// To avoid thundering herd on etcd (e.g. on master upgrades), we explicitly
// switch off pagination to force listing from watch cache (if enabled).
// With the existing semantic of RV (result is at least as fresh as provided RV),
// this is correct and doesn't lead to going back in time.
//
// We also don't turn off pagination for ResourceVersion="0", since watch cache
// is ignoring Limit in that case anyway, and if watch cache is not enabled
// we don't introduce regression.
pager.PageSize = 0
}
list, paginatedResult, err = pager.List(context.Background(), options)
if isExpiredError(err) || isTooLargeResourceVersionError(err) {
r.setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable(true)
// Retry immediately if the resource version used to list is unavailable.
// The pager already falls back to full list if paginated list calls fail due to an "Expired" error on
// continuation pages, but the pager might not be enabled, the full list might fail because the
// resource version it is listing at is expired or the cache may not yet be synced to the provided
// resource version. So we need to fallback to resourceVersion="" in all to recover and ensure
// the reflector makes forward progress.
list, paginatedResult, err = pager.List(context.Background(), metav1.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: r.relistResourceVersion()})
}
close(listCh)
}()
select {
case <-stopCh:
return nil
case r := <-panicCh:
panic(r)
case <-listCh:
}
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to list %v: %v", r.expectedTypeName, err)
}
// We check if the list was paginated and if so set the paginatedResult based on that.
// However, we want to do that only for the initial list (which is the only case
// when we set ResourceVersion="0"). The reasoning behind it is that later, in some
// situations we may force listing directly from etcd (by setting ResourceVersion="")
// which will return paginated result, even if watch cache is enabled. However, in
// that case, we still want to prefer sending requests to watch cache if possible.
//
// Paginated result returned for request with ResourceVersion="0" mean that watch
// cache is disabled and there are a lot of objects of a given type. In such case,
// there is no need to prefer listing from watch cache.
if options.ResourceVersion == "0" && paginatedResult {
r.paginatedResult = true
}
r.setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable(false) // list was successful
initTrace.Step("Objects listed")
listMetaInterface, err := meta.ListAccessor(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to understand list result %#v: %v", list, err)
}
resourceVersion = listMetaInterface.GetResourceVersion()
initTrace.Step("Resource version extracted")
items, err := meta.ExtractList(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to understand list result %#v (%v)", list, err)
}
initTrace.Step("Objects extracted")
if err := r.syncWith(items, resourceVersion); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("unable to sync list result: %v", err)
}
initTrace.Step("SyncWith done")
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
initTrace.Step("Resource version updated")
return nil
}(); err != nil {
return err
}
// 定时Resync机制
resyncerrc := make(chan error, 1)
cancelCh := make(chan struct{})
defer close(cancelCh)
go func() {
resyncCh, cleanup := r.resyncChan()
defer func() {
cleanup() // Call the last one written into cleanup
}()
for {
select {
case <-resyncCh:
case <-stopCh:
return
case <-cancelCh:
return
}
if r.ShouldResync == nil || r.ShouldResync() {
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: forcing resync", r.name)
// 调用DeltaFIFO的Resync
if err := r.store.Resync(); err != nil {
resyncerrc <- err
return
}
}
cleanup()
resyncCh, cleanup = r.resyncChan()
}
}()
// Watch处理
for {
// give the stopCh a chance to stop the loop, even in case of continue statements further down on errors
select {
case <-stopCh:
return nil
default:
}
timeoutSeconds := int64(minWatchTimeout.Seconds() * (rand.Float64() + 1.0))
options = metav1.ListOptions{
ResourceVersion: resourceVersion,
// We want to avoid situations of hanging watchers. Stop any wachers that do not
// receive any events within the timeout window.
TimeoutSeconds: &timeoutSeconds,
// To reduce load on kube-apiserver on watch restarts, you may enable watch bookmarks.
// Reflector doesn't assume bookmarks are returned at all (if the server do not support
// watch bookmarks, it will ignore this field).
AllowWatchBookmarks: true,
}
// start the clock before sending the request, since some proxies won't flush headers until after the first watch event is sent
start := r.clock.Now()
w, err := r.listerWatcher.Watch(options)
if err != nil {
// If this is "connection refused" error, it means that most likely apiserver is not responsive.
// It doesn't make sense to re-list all objects because most likely we will be able to restart
// watch where we ended.
// If that's the case begin exponentially backing off and resend watch request.
// Do the same for "429" errors.
if utilnet.IsConnectionRefused(err) || apierrors.IsTooManyRequests(err) {
<-r.initConnBackoffManager.Backoff().C()
continue
}
return err
}
if err := r.watchHandler(start, w, &resourceVersion, resyncerrc, stopCh); err != nil {
if err != errorStopRequested {
switch {
case isExpiredError(err):
// Don't set LastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable - LIST call with ResourceVersion=RV already
// has a semantic that it returns data at least as fresh as provided RV.
// So first try to LIST with setting RV to resource version of last observed object.
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: watch of %v closed with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
case apierrors.IsTooManyRequests(err):
klog.V(2).Infof("%s: watch of %v returned 429 - backing off", r.name, r.expectedTypeName)
<-r.initConnBackoffManager.Backoff().C()
continue
default:
klog.Warningf("%s: watch of %v ended with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
}
}
return nil
}
}
}
func (r *Reflector) watchHandler(start time.Time, w watch.Interface, resourceVersion *string, errc chan error, stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
...
loop:
for {
select {
case <-stopCh:
return errorStopRequested
case err := <-errc:
return err
case event, ok := <-w.ResultChan():
if !ok {
break loop
}
if event.Type == watch.Error {
return apierrors.FromObject(event.Object)
}
if r.expectedType != nil {
if e, a := r.expectedType, reflect.TypeOf(event.Object); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected type %v, but watch event object had type %v", r.name, e, a))
continue
}
}
if r.expectedGVK != nil {
if e, a := *r.expectedGVK, event.Object.GetObjectKind().GroupVersionKind(); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected gvk %v, but watch event object had gvk %v", r.name, e, a))
continue
}
}
meta, err := meta.Accessor(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
continue
}
newResourceVersion := meta.GetResourceVersion()
// 按类型处理资源事件
switch event.Type {
case watch.Added:
// 将对象存入DeltaFIFO中
err := r.store.Add(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to add watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Modified:
err := r.store.Update(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to update watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Deleted:
// TODO: Will any consumers need access to the "last known
// state", which is passed in event.Object? If so, may need
// to change this.
err := r.store.Delete(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to delete watch event object (%#v) from store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Bookmark:
// A `Bookmark` means watch has synced here, just update the resourceVersion
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
}
*resourceVersion = newResourceVersion
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(newResourceVersion)
if rvu, ok := r.store.(ResourceVersionUpdater); ok {
rvu.UpdateResourceVersion(newResourceVersion)
}
eventCount++
}
}
...
}
5 controller.processLoop循环处理资源变化事件
func (c *controller) processLoop() {
for {
// 从DeltaFIFO中Pop事件,调用c.config.Process处理,即s.HandleDeltas
obj, err := c.config.Queue.Pop(PopProcessFunc(c.config.Process))
if err != nil {
if err == ErrFIFOClosed {
return
}
if c.config.RetryOnError {
// This is the safe way to re-enqueue.
c.config.Queue.AddIfNotPresent(obj)
}
}
}
}
6 sharedIndexInformer.HandleDeltas 处理事件,存储到缓存indexer中,并调用distribute分发事件,在distribute中调用各个listener的add加入channel
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) HandleDeltas(obj interface{}) error {
s.blockDeltas.Lock()
defer s.blockDeltas.Unlock()
// from oldest to newest
for _, d := range obj.(Deltas) {
switch d.Type {
case Sync, Replaced, Added, Updated:
s.cacheMutationDetector.AddObject(d.Object)
if old, exists, err := s.indexer.Get(d.Object); err == nil && exists {
// indexer缓存存在则更新
if err := s.indexer.Update(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
isSync := false
switch {
case d.Type == Sync:
// Sync events are only propagated to listeners that requested resync
isSync = true
case d.Type == Replaced:
if accessor, err := meta.Accessor(d.Object); err == nil {
if oldAccessor, err := meta.Accessor(old); err == nil {
// Replaced events that didn't change resourceVersion are treated as resync events
// and only propagated to listeners that requested resync
isSync = accessor.GetResourceVersion() == oldAccessor.GetResourceVersion()
}
}
}
// 分发处理,将事件通过channel发送到listener处理
s.processor.distribute(updateNotification{oldObj: old, newObj: d.Object}, isSync)
} else {
// indexer缓存新建对象
if err := s.indexer.Add(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(addNotification{newObj: d.Object}, false)
}
case Deleted:
// indexer删除缓存对象
if err := s.indexer.Delete(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
s.processor.distribute(deleteNotification{oldObj: d.Object}, false)
}
}
return nil
}
7 sharedProcessor.run 启动各个listener的run与pop
func (p *sharedProcessor) run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
func() {
p.listenersLock.RLock()
defer p.listenersLock.RUnlock()
for _, listener := range p.listeners {
// 调用注册的回调函数处理事件
p.wg.Start(listener.run)
// 获得addCh来的事件,即HandleDeltas中distribute执行各个listener.add
p.wg.Start(listener.pop)
}
p.listenersStarted = true
}()
<-stopCh
p.listenersLock.RLock()
defer p.listenersLock.RUnlock()
for _, listener := range p.listeners {
close(listener.addCh) // Tell .pop() to stop. .pop() will tell .run() to stop
}
p.wg.Wait() // Wait for all .pop() and .run() to stop
}
func (p *processorListener) run() {
stopCh := make(chan struct{})
wait.Until(func() {
for next := range p.nextCh {
switch notification := next.(type) {
case updateNotification:
// 处理回调,为sharedIndexInformer.AddEventHandler注册的回调处理函数
p.handler.OnUpdate(notification.oldObj, notification.newObj)
case addNotification:
p.handler.OnAdd(notification.newObj)
case deleteNotification:
p.handler.OnDelete(notification.oldObj)
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unrecognized notification: %T", next))
}
}
// the only way to get here is if the p.nextCh is empty and closed
close(stopCh)
}, 1*time.Second, stopCh)
}
Resync机制
Resync 机制的引入,定时将 Indexer 缓存事件重新同步到 Delta FIFO 队列中,在处理 SharedInformer 事件回调时,让处理失败的事件重新处理。并且通过入队前判断 FIFO 队列中是否已经有了更新版本的 event,来决定是否丢弃 Indexer 缓存不进行 Resync 入队。在处理 Delta FIFO 队列中的 Resync 的事件数据时,触发 onUpdate 回调来让事件重新处理。下面看下DeltaFIFO中Resync代码:
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Resync() error {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
if f.knownObjects == nil {
return nil
}
// 从indexer中获取keys进行处理
keys := f.knownObjects.ListKeys()
for _, k := range keys {
if err := f.syncKeyLocked(k); err != nil {
return err
}
}
return nil
}
func (f *DeltaFIFO) syncKeyLocked(key string) error {
// 根据key获取资源对象
obj, exists, err := f.knownObjects.GetByKey(key)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Unexpected error %v during lookup of key %v, unable to queue object for sync", err, key)
return nil
} else if !exists {
klog.Infof("Key %v does not exist in known objects store, unable to queue object for sync", key)
return nil
}
// 如果FIFO中相同Key的资源对象,说明新event,这时可以不进行Resync处理
id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
if len(f.items[id]) > 0 {
return nil
}
// 重新放入 DeltaFIFO 队列
if err := f.queueActionLocked(Sync, obj); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("couldn't queue object: %v", err)
}
return nil
}
在《Programming Kubernetes》对Resync进制进行了阐述,可以帮助我们理解
在分布式系统中,有许多操作在并行执行,事件可能会以任意顺序异步到达。 如果我们的 controller 逻辑有问题,状态机出现一些错误或外部服务故障时,就很容易丢失事件,导致我们没有处理所有事件。 因此,我们必须更深入地研究如何应对这些问题。 在图中,您可以看到可用的不同方案:
- 仅使用边缘驱动逻辑的示例,其中可能错过第二个的状态更改事件。
- 边缘触发逻辑的示例,在处理事件时始终会获取最新状态(即水平)。换句话说,逻辑是边缘触发的(edge-triggered),但是水平驱动的(level-driven)。
- 该示例的逻辑是边缘触发,水平驱动的,但同时还附加了定时同步的能力。
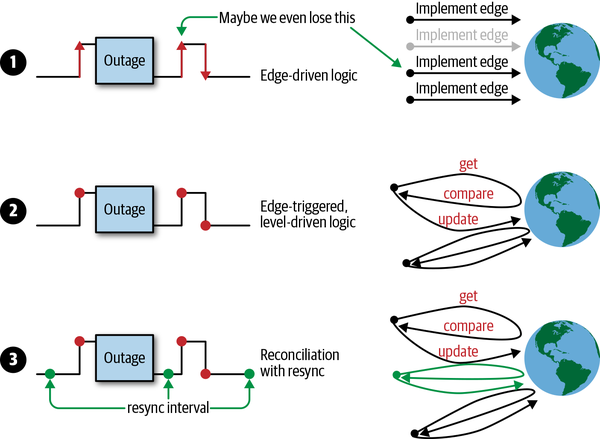
考虑到仅使用单一的边缘驱动触发会产生的问题,Kubernetes controller 通常采用第 3 种方案。